- Recommended name
- β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine
- Synonyms
- α-Amino-β-methylaminopropionic acid, (S)-2-Amino-3-(methylamino)propanoic acid
- Recommended acronym
- BMAA
- Abbreviation
Progenitors
- Name
- Skeletonema marinoi
- Note
- Diatoms: A Novel Source for the Neurotoxin BMAA in Aquatic Environments AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Gymnodinium catenatum
- Note
- BMAA in shellfish from two Portuguese transitional water bodies suggests the marine dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum as a potential BMAA source AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Thalassiosira pseudonana
- Note
- β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and isomers: Distribution in different food web compartments of Thau lagoon, French Mediterranean Sea AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Leptolyngbya
- Note
- Strategy for quantifying trace levels of BMAA in cyanobacteria by LC/MS/MS AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Planktoniella blanda
- Note
- Putative biosynthesis mechanism of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in marine diatoms based on a transcriptomics approach HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Thalassiosira gravida
- Note
- Putative biosynthesis mechanism of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in marine diatoms based on a transcriptomics approach HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Thalassiosira
- Note
- Diatoms: A Novel Source for the Neurotoxin BMAA in Aquatic Environments; Production of BMAA and DAB by diatoms (Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Chaetoceros sp., Chaetoceros calcitrans and, Thalassiosira pseudonana) and bacteria isolated from a diatom culture; Kinetics of β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid (DAB) production by diatoms: the effect of nitrogen; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China AQC UPLC-MS/MS;HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Chaetoceros
- Note
- β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and isomers: Distribution in different food web compartments of Thau lagoon, French Mediterranean Sea; Production of BMAA and DAB by diatoms (Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Chaetoceros sp., Chaetoceros calcitrans and, Thalassiosira pseudonana) and bacteria isolated from a diatom culture; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China AQC UPLC-MS/MS;HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Phaeodactylum tricornutum
- Note
- β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and isomers: Distribution in different food web compartments of Thau lagoon, French Mediterranean Sea; Production of BMAA and DAB by diatoms (Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Chaetoceros sp., Chaetoceros calcitrans and, Thalassiosira pseudonana) and bacteria isolated from a diatom culture; Kinetics of β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid (DAB) production by diatoms: the effect of nitrogen AQC UPLC-MS/MS;HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Halamphora coffeaeformis
- Note
- Systematic detection of BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) and DAB (2,4-diaminobutyric acid) in mollusks collected in shellfish production areas along the French coasts HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Navicula
- Note
- Kinetics of β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid (DAB) production by diatoms: the effect of nitrogen AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Chaetoceros decipiens
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudo-nitzschia lundholmiae
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudo-nitzschia bipertita
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudo-nitzschia simulans
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudo-nitzschia
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudo-nitzschia fraudulenta
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Planktoniella blanda
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China Putative biosynthesis mechanism of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in marine diatoms based on a transcriptomics approach HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Thalassiosira lundiana
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China Putative biosynthesis mechanism of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in marine diatoms based on a transcriptomics approach HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Thalassiosira minima
- Note
- Putative biosynthesis mechanism of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in marine diatoms based on a transcriptomics approach HILIC-MS/MS
Vector Species
- Name
- Osmerus eperlanus
- Note
- Transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin within a temperate aquatic ecosystem suggests pathways for human exposure AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Scophthalmus maximus
- Note
- Transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin within a temperate aquatic ecosystem suggests pathways for human exposure AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Clupea harengus
- Note
- Transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin within a temperate aquatic ecosystem suggests pathways for human exposure AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Coregonus lavaretus
- Note
- Transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin within a temperate aquatic ecosystem suggests pathways for human exposure AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Ostrea edulis
- Note
- Transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin within a temperate aquatic ecosystem suggests pathways for human exposure; Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets AQC HPLC-MS/MS; AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Callinectes sapidus
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pinctada margaritifera
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Sphoeroides parvus
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mytilus edulis
- Note
- Transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin within a temperate aquatic ecosystem suggests pathways for human exposure; Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets; Seafood sold in Sweden contains BMAA: A study of free and total concentrations with UHPLC-MS/MS and dansyl chloride derivatization; A new method for analysis of underivatized free β-methylamino-alanine: Validation and method comparison AQC HPLC-MS/MS; AQC UPLC-MS/MS;DNS HPLC-MS/MS;HILIC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pseudorasbora parva
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Rhodeus sinensis
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Panulirus
- Note
- Detection of cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine within shellfish in the diet of an ALS patient in Florida AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Corbicula
- Note
- Biomagnification characteristics and health risk assessment of the neurotoxin BMAA in freshwater aquaculture products of Taihu Lake Basin, China
- Name
- Sphoeroides spengleri
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Lutjanus griseus
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Gerreidae
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Acanthostracion quadricornis
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Haemulon parra
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Alligator
- Note
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Callinectes sapidus
- Note
- Detection and quantification of β-methylamino-L-alanine in aquatic invertebrates; Linking β-methylamino-L-alanine exposure to sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Annapolis, MD AQC LC-MS/MS;AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mytilus galloprovincialis
- Note
- Dietary BMAA Exposure in an Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Cluster from Southern France; Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China; Matrix Effect of Diverse Biological Samples Extracted with Different Extraction Ratios on the Detection of β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine by Two Common LC-MS/MS Analysis Methods AQC UPLC-MS/MS;HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Cerastoderma edule
- Note
- BMAA in shellfish from two Portuguese transitional water bodies suggests the marine dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum as a potential BMAA source AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Caridea
- Note
- Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Pleuronectes platessa
- Note
- Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Clupea harengus
- Note
- Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Salvelinus alpinus
- Note
- Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Eriocheir
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Macrobrachium
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Procambarus clarkii
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Carassius auratus
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Cyprinus
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Erythroculter
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Hemiramphus
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Hypophthalmichthys molitrix
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Neosalanx
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Parabramis pekinensis
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Pelteobagrus
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Protosalanx hyalocranius
- Note
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk AQC HPLC–MS/MS
- Name
- Cyprinus carpio
- Note
- Detection of Cyanotoxins, β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and Microcystins, from a Lake Surrounded by Cases of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis AQC LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Abramis brama
- Note
- Biotransfer of β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a Eutrophicated Freshwater Lake AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Perca fluviatilis
- Note
- Biotransfer of β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a Eutrophicated Freshwater Lake AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Esox lucius
- Note
- Biotransfer of β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a Eutrophicated Freshwater Lake AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Sander lucioperca
- Note
- Biotransfer of β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a Eutrophicated Freshwater Lake AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Gymnocephalus cernua
- Note
- Biotransfer of β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a Eutrophicated Freshwater Lake AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Anguilla anguilla
- Note
- Biotransfer of β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a Eutrophicated Freshwater Lake AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Perna canaliculus
- Note
- Seafood sold in Sweden contains BMAA: A study of free and total concentrations with UHPLC-MS/MS and dansyl chloride derivatization DNS UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Placopecten magellanicus
- Note
- Seafood sold in Sweden contains BMAA: A study of free and total concentrations with UHPLC-MS/MS and dansyl chloride derivatization DNS UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mytilus
- Note
- New Typical Vector of Neurotoxin β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine (BMAA) in the Marine Benthic Ecosystem; Systematic detection of BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) and DAB (2,4-diaminobutyric acid) in mollusks collected in shellfish production areas along the French coasts; Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Solen strictus
- Note
- New Typical Vector of Neurotoxin β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine (BMAA) in the Marine Benthic Ecosystem HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Neverita didyma
- Note
- New Typical Vector of Neurotoxin β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine (BMAA) in the Marine Benthic Ecosystem; Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Crassostrea
- Note
- Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets; Systematic detection of BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) and DAB (2,4-diaminobutyric acid) in mollusks collected in shellfish production areas along the French coasts; Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China; Matrix Effect of Diverse Biological Samples Extracted with Different Extraction Ratios on the Detection of β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine by Two Common LC-MS/MS Analysis Methods AQC LC-MS/MS;HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Phocoena
- Note
- A collaborative evaluation of LC-MS/MS based methods for BMAA analysis: Soluble bound BMAA found to be an important fraction HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Galeocerdo cuvier
- Note
- Cyanobacterial Neurotoxin BMAA and Mercury in Sharks AQC UPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Chlamys
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Patinopecten
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Clinocardium
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Ruditapes philippinarum
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mactra
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Atrina pectinata
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks; Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mactra
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Callista chinensis
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Dosinia japonica
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Tegillarca granosa
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Saxidomus purpurata
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Callista
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Cyclina sinensis
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Gomphina
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mercenaria mercenaria
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Solen strictus
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Meretrix meretrix
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mactra chinensis
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Neptunea arthritica
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Neptunea
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Neptunea cumingii
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Laguncula pulchella
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Rapana venosa
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Reishia luteostoma
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Turbo
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Asterias amurensis
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Smilium scorpio
- Note
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Macrobrachium
- Note
- Biomagnification characteristics and health risk assessment of the neurotoxin BMAA in freshwater aquaculture products of Taihu Lake Basin, China AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Eriocheir sinensis
- Note
- Biomagnification characteristics and health risk assessment of the neurotoxin BMAA in freshwater aquaculture products of Taihu Lake Basin, China AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Ctenopharyngodon idella
- Note
- Biomagnification characteristics and health risk assessment of the neurotoxin BMAA in freshwater aquaculture products of Taihu Lake Basin, China AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Mylopharyngodon piceus
- Note
- Biomagnification characteristics and health risk assessment of the neurotoxin BMAA in freshwater aquaculture products of Taihu Lake Basin, China AQC HPLC-MS/MS
- Name
- Sinonovacula constricta
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Solenocera melantho
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Zoarces elongatus
- Note
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China HILIC-MS/MS
- Name
- Patinopecten
- Note
- Matrix Effect of Diverse Biological Samples Extracted with Different Extraction Ratios on the Detection of β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine by Two Common LC-MS/MS Analysis Methods HILIC-MS/MS
References
- Jiang, L., 2014
- Diatoms: A Novel Source for the Neurotoxin BMAA in Aquatic Environments
- Zhao, P., 2022
- Matrix Effect of Diverse Biological Samples Extracted with Different Extraction Ratios on the Detection of β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine by Two Common LC-MS/MS Analysis Methods
- Jonasson, S., 2010
- Transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin within a temperate aquatic ecosystem suggests pathways for human exposure
- Brand, L. E., 2010
- Cyanobacterial blooms and the occurrence of the neurotoxin, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), in South Florida aquatic food webs
- Christensen, Stephanie J., 2012
- Detection and quantification of β-methylamino-L-alanine in aquatic invertebrates
- Contardo-Jara, V., 2013
- Linking β-methylamino-L-alanine exposure to sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Annapolis, MD
- Jiang, L., 2013
- Strategy for quantifying trace levels of BMAA in cyanobacteria by LC/MS/MS
- Jiang, L., 2013
- Strategy for quantifying trace levels of BMAA in cyanobacteria by LC/MS/MS
- Masseret, E., 2013
- Dietary BMAA Exposure in an Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Cluster from Southern France
- Lage, S., 2014
- BMAA in shellfish from two Portuguese transitional water bodies suggests the marine dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum as a potential BMAA source
- Jiang, L., 2014
- Quantification of neurotoxin BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) in seafood from Swedish markets
- Jiao, Y., 2014
- Occurrence and transfer of a cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-methylamino-L-alanine within the aquatic food webs of Gonghu Bay (Lake Taihu, China) to evaluate the potential human health risk
- Banack, S. A., 2014
- Detection of cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine within shellfish in the diet of an ALS patient in Florida
- Banack, S. A., 2015
- Detection of Cyanotoxins, β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and Microcystins, from a Lake Surrounded by Cases of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Lage, S., 2015
- Biotransfer of β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a Eutrophicated Freshwater Lake
- Salomonsson, M. L., 2015
- Seafood sold in Sweden contains BMAA: A study of free and total concentrations with UHPLC-MS/MS and dansyl chloride derivatization
- Reveillon, D., 2015
- β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and isomers: Distribution in different food web compartments of Thau lagoon, French Mediterranean Sea
- Li, A., 2016
- New Typical Vector of Neurotoxin β-N-Methylamino-L-Alanine (BMAA) in the Marine Benthic Ecosystem
- Reveillon, D., 2016
- Production of BMAA and DAB by diatoms (Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Chaetoceros sp., Chaetoceros calcitrans and, Thalassiosira pseudonana) and bacteria isolated from a diatom culture
- Reveillon, D., 2016
- Systematic detection of BMAA (β-N-methylamino-L-alanine) and DAB (2,4-diaminobutyric acid) in mollusks collected in shellfish production areas along the French coasts
- Edwards, C., 2016
- A collaborative evaluation of LC-MS/MS based methods for BMAA analysis: Soluble bound BMAA found to be an important fraction
- Rosén, J., 2016
- A new method for analysis of underivatized free β-methylamino-alanine: Validation and method comparison
- Lage, Sandra, 2018
- Kinetics of β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid (DAB) production by diatoms: the effect of nitrogen
- Li, A., 2018
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks
- Wu, X., 2019
- Biomagnification characteristics and health risk assessment of the neurotoxin BMAA in freshwater aquaculture products of Taihu Lake Basin, China
- Wang, C., 2021
- Food web biomagnification of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in a diatom-dominated marine ecosystem in China
- Li, A., 2023
- Putative biosynthesis mechanism of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine in marine diatoms based on a transcriptomics approach
- Structure
-
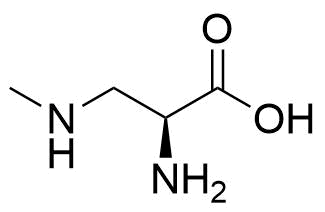
- Formula
- C4H10N2O2
- Exact mono-isotopic mass
- 118.0742
- Molfile
- n/a
- Alternative molfiles
- n/a
- SMILES
- CNCC(N)C(O)=O
- Alternative SMILES
- CNC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
- InChi key
- UJVHVMNGOZXSOZ-VKHMYHEASA-N
- Alternative InChi keys
- n/a
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C4H10N2O2/c1-6-2-3(5)4(7)8/h3,6H,2,5H2,1H3,(H,7,8)/t3-/m0/s1
- Alternative InChis
- Spectra available
- Unknown
- Chem files
References
- A. Vega, 1967
- α-Amino-β-methylaminopropionic acid, a new amino acid from seeds of Cycas circinalis
- Nunn, P. B., 1989
- The interaction of β-N-methylamino-L-alanine with bicarbonate: an 1H-NMR study
- Certified
- False
- Certified links
-
-
n/a
- Non certified reference material
- Unknown
Chemical analysis
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- False
- Validated
- True
- Official
- n/a
Structure recognition assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Functional assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Animal assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- False
- Validated
- True
- Official
- n/a
References
- Li, A., 2018
- Ubiquity of the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine and its isomers confirmed by two different mass spectrometric methods in diverse marine mollusks
- Regulatory status
- False
- Human toxic syndrome(s)
- n/a
- Organ system toxicity
- Neurotoxicity
- Risk assessment
- True
- Molecular targets known
- Unknown
- Molecular targets
- n/a
- Toxic to aquatic animals
- True
- TEF available
- Unknown
Risk assessment References
- Wu, X., 2019
- Biomagnification characteristics and health risk assessment of the neurotoxin BMAA in freshwater aquaculture products of Taihu Lake Basin, China
- Notes